

functional neurological disorder
What is Functional Neurological Disorder (FND)?
Functional Neurological Disorder (also known as FND) is a medical condition in which there is a problem with the functioning of the nervous system and the ways in which the brain and the body sends and receives signals.
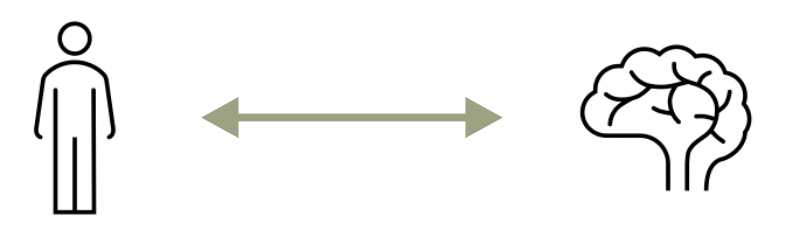
When the nervous system is functioning normally the brain and the body send and receive messages controlling movement and sensory perception.
Imagine the brain as a computer which contains hardware and software. The brain’s software controls how your brain communicates with itself, the outside world, and also the body.
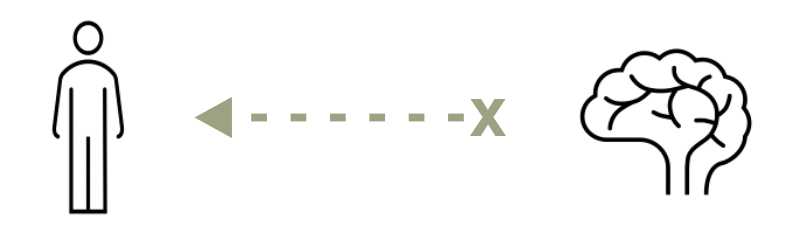
When the nervous system is functioning abnormally the brain fails to communicate neural messages to the body leading to movement difficulties.
Functional Neurological Disorders are like glitches in the software of the brain. This can cause the hardware to function abnormally and react differently to the environment.
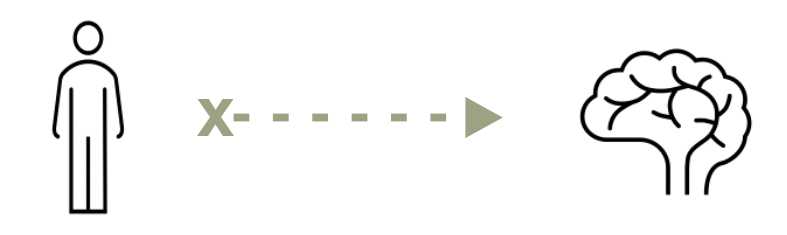
When the nervous system is functioning abnormally the body’s sensory system fails to communicate neural messages to the brain leading to sensory difficulties.
Treatment involves recognising these glitches and learning how to troubleshoot them.
Specific symptoms of communication may occur. To be noted – these specific symptoms can co-occur. A person may experience a range of symptoms at different times.
Communication symptoms
- Functional voice disorders
- Dysphonia simply means ‘disordered voice’
- Aphonia refers to ’complete loss of voice’
- Odynophobia refers ‘pain using voice’
- Vocal fatigue
- Mutational falsetto or puberphonia refers to ‘high pitched voice after puberty’
- Functional stuttering disorder
- Most commonly associated with involuntary sound repetition in words
- Functional articulation disorder (speech sound production)
- Functional language disorder
Globus pharyngeus (functional)
- Symptoms presents as a recurrent, non-painful but uncomfortable sensation of a lump in the throat, in the absence of dysphagia, odynophobia, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or an oesophageal motility disorder.
Functional Dysphagia symptoms
- Symptoms are most often associated with the oral and pharyngeal phase of the swallow.
- Symptoms include ‘hard to swallow’, pain on swallowing, choking sensations and coughing
Cough and vocal cord dysfunction
- Laryngeal hypersensitivity syndrome
What Causes FND?
- Several potential risk factors have been identified. There is no single cause. FND is often the result of multiple risk factors that overwhelm the nervous system leading to its dysfunction. For some people, a trigger or cause will never be found.
- No underlying or identifiable trigger
- Physical or emotional trauma
- Accident, injury, or surgery
- Any pre-existing physical health condition
- Any pre-existing mental health condition
- Long term stress
How common is FND?
FND is one of the most common diagnoses in neurologic practice and the second most common reason for a neurologic consultation after a headache. FND is estimated to be experienced by around 50 people per 100,000 population. In a recent Australian study of an outpatient neurology clinic, 15% of new presentations received a primary diagnosis of FND, whilst other studies find that up to 30% have at least some functional element as part of their symptoms.
It’s important to be aware of the following:
- Communication, swallowing, and cough symptoms resulting from functional neurological disorder are commonly encountered by speech pathologists.
- A speech pathologist has the existing skillset and expertise to:
-
- Assist with differential diagnosis (i.e., a positive diagnosis based on symptoms consistent with Functional Neurological Disorder)
- Provide treatment of functional communication, swallowing and cough disorders
- Collaborate with other health professionals as part of the multidisciplinary team.
A speech pathologist can:
- Take a comprehensive case history;
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the presenting symptoms (i.e., communication, swallowing and/or cough symptoms);
- Collaborate with the client (and family) to provide a person-centered treatment plan (inclusive of Functional Neurological Disorder education and direction to other resources) based on the client’s treatment needs and goals;
- Collaborate with other members of the clinical team (e.g., physiotherapist, psychologist, occupational therapist) as required.
Speech pathologists are trained to assess, diagnose, provide treatment and advocate for people with Functional Neurological Disorder (FND) and their families. Please contact connect2community speech pathology if you have any concerns or questions regarding FND or a recent diagnosis of FND.
PHONE 0411 864 386
EMAIL info@connect2community.au
